Writing for Accessibility
What
When writing for your website or documents that will uploaded there, keep your text as short and simple as possible. The goal is to write at a 10th-grade level.
Why
Simplifying the writing on a website benefits everyone; those with cognitive issues, people for whom English is a second language, or people on the go.
How
-
Avoid acronyms and always spell out on first reference
-
Use capitalization sparingly
-
Do not underline text that is not a link; underlining text is a website convention for links
-
Have something to say that readers want to know
-
Choose simple words
-
Write short sentences
-
Keep paragraphs short
-
Eliminate fluff words
-
Don’t ramble
-
Don’t repeat yourself
-
Edit ruthlessly
Tools
A readability checker allows you to either check a URL or enter in text. It returns a grade level that users must be to understand the text entered.
The goal is for content to be at a grade level 10.
If your content comes back higher, around grade level 13 for instance, don't worry. But if your content comes back at a grade level 21, you must go back and simplify.
What
Use the built-in headings in the text editor to create sections on the page.
Why
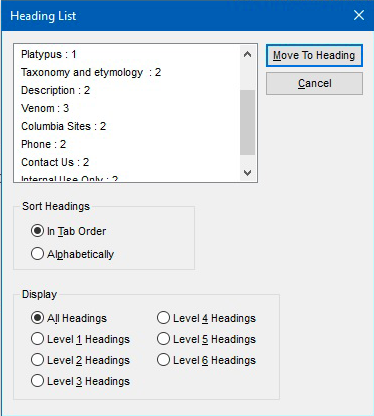
Most people use headers and subtitles to scan pages, particularly those using screen readers. In fact, users of the JAWS screen reader are able to aggregate all headers on a given screen for easier scanning. Users can use this list to select content to read. So use headers to "chunk" your content and make the header titles easy-to-understand descriptions of the content that follows.
How
- Use the built-in headers in the text editor
- Use the text editor built-in formatting to create headings and NOT your own formatting (e.g., capitalization, bold, italics, etc.)
-
Use proper order of headings as you would with a formal outline
-
Your first header must always be Heading 2
-
Do not skip any levels.
CORRECT: Heading 2 followed by Heading 3
INCORRECT: Heading 2 followed by Heading 4
-
What
Make sure users can predict where links navigate even if the link text is taken out of context.
Why
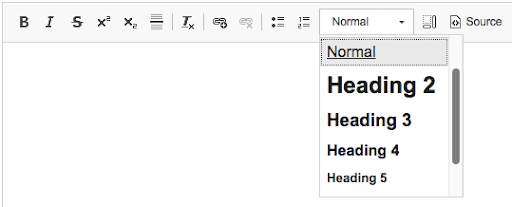
People using screen readers are able to aggregate links on a given screen for easier scanning. Users can use this list to select the link for navigation. All users benefit from an accurate description of where a link will take them.
How
- Never use text "Click Here" or "Read More" to describe a link
- Links should be descriptive
- Links can be longer than one or two words to make sense
What
When creating lists or sections on a page, use the built-in lists and headers.
Why
Screen readers understand built-in formatting and can appropriately format it. Formatting created offhand is not understood and will not be properly formatted by screen readers.
How
Use the built-in formatting for bulleted lists, numbered lists, and headers